- BACKGROUND
- 1. INCORRECT CHICK BREED SELECTION
- 2. POOR QUALITY FEED
- 3. IMPROPER HOUSING CONDITIONS
- 4. IGNORING BIOSECURITY MEASURES
- 5. INADEQUATE RECORD KEEPING
- 6. OVERLOOKING REGULATORY COMPLIANCE
- 7. INCONSISTENT WATER SUPPLY
- 8. INADEQUATE MARKETING STRATEGIES
- 9. NEGLECTING ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
- 10. FAILURE TO INVEST IN TRAINING AND EDUCATION
- FINAL THOUGHTS
BACKGROUND
Organic chicken farming is popular among both new and experienced farmers due to its profitability, health benefits, and growing consumer demand. However, success in this field is not always straightforward. Mistakes often occur due to a lack of knowledge or experience, which can hinder productivity, profitability, and animal welfare. This article dives into the top 10 common mistakes in organic chicken farming and provides practical solutions to overcome them. Whether you’re just starting or looking to enhance your farm’s efficiency, this guide will help you balance quality, sustainability, and regulatory compliance to achieve your farming goals.
For new farmers, it’s vital to familiarize yourself with the basics. Begin with our Beginner’s Guide to Raising Chickens Naturally or explore our guide on setting up a small-scale chicken farm to ensure your foundation is strong.
1. INCORRECT CHICK BREED SELECTION
Choosing the right breed involves considering factors like climate, farm setup, production goals, and disease resistance. Breeds like Cornish Cross, though popular in commercial farming, may not be the best for organic settings due to their need for specialized feed. Instead, heritage breeds like Rhode Island Red and Sussex are better suited for organic environments, as they are hardy, adaptable, and good foragers.
Best Breeds for Organic Chicken Farming (Expanded)
Breed | Adaptability | Egg Production | Meat Quality | Foraging Ability |
Rhode Island Red | High | High | Moderate | Excellent |
Sussex | High | Moderate | High | Good |
Plymouth Rock | Moderate | High | High | Good |
- Rhode Island Red: These chickens can adapt to both free-range and small coop environments, making them versatile for various organic setups.
- Sussex: In addition to high-quality meat, they are known for their consistent egg production, making them suitable for dual-purpose farming.
- Plymouth Rock: While they require more space, their calm temperament and reliable productivity make them a favorite among organic farmers.
Solution: Before purchasing chicks, evaluate the breed’s compatibility with your farm environment. Talk to local farmers and use resources like Top 15 Chicken Breeds for Sustainable Farming for more information.
Example: A farmer in Florida replaced Cornish Cross with Plymouth Rock to reduce feed costs and increase foraging efficiency, achieving a 20% boost in profits over 18 months.
2. POOR QUALITY FEED
The importance of organic feed cannot be overstated. Many farmers try to cut costs by using low-cost feed, but this often results in nutritional deficiencies. Chickens need a balanced diet rich in proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fats to grow well and lay quality eggs.
Essential Components of Organic Feed
- Carbohydrates: Grains like corn and barley provide energy for daily activities.
- Proteins: Ingredients like soybeans, fishmeal, and alfalfa support muscle development and egg production.
- Fats: Flaxseed and sunflower seeds are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids, essential for healthy egg yolks.
- Vitamins & Minerals: Supplements like kelp meal provide iodine, while grit aids digestion.
For more feeding tips, visit our Feeding Chickens – The Natural Way guide. Also, check out Organic Valley’s Feed Guide for expert advice on feed composition.
Solution: Invest in high-quality organic feed that aligns with chickens’ nutritional needs. Adjust the diet seasonally to support their health and productivity.
Example: A farm in Kentucky transitioned to high-protein organic feed during the winter months, which led to a 15% increase in egg size and consistency.
3. IMPROPER HOUSING CONDITIONS
A well-designed coop is essential for chicken health. Inadequate housing can lead to issues like overcrowding, poor ventilation, and predator risks, all of which can decrease productivity.
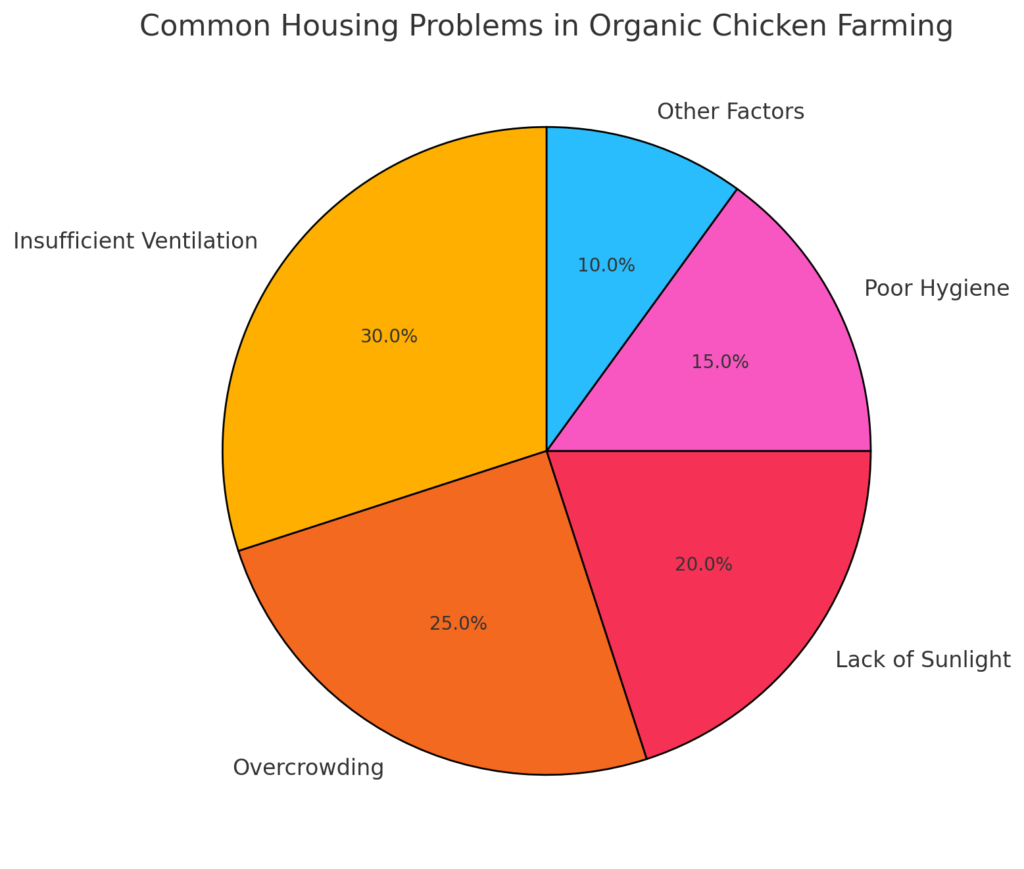
Pie chart: Insufficient ventilation (30%), overcrowding (25%), lack of sunlight (20%), and poor hygiene (15%) are the main housing issues.
Improved Housing Solutions
- Adjustable Ventilation: Installing adjustable vents can help regulate airflow based on weather conditions, reducing humidity and preventing respiratory issues.
- Deep Litter System: This bedding method not only maintains coop cleanliness but also provides warmth and reduces waste management efforts.
- Perches & Nest Boxes: Include perches and separate nest boxes to ensure comfort and prevent egg breakage.
Solution: Design the coop to accommodate all seasons. Use materials that are easy to clean and maintain. Explore our guide on setting up a small-scale chicken farm for practical coop designs.
Example: After integrating an automatic ventilation system, a farmer in Alabama saw a 25% increase in egg production and a significant decrease in respiratory infections.
4. IGNORING BIOSECURITY MEASURES
Biosecurity is the backbone of disease prevention. Farmers often neglect simple measures like footbaths, which can prevent the spread of diseases. It’s crucial to train farmworkers on proper sanitation and handling of chickens.
Key Biosecurity Practices
- Footbaths at Entry Points: Use disinfectant solutions at all entry points to prevent disease transmission.
- Separate Clothing: Have separate clothing and footwear for farm use to prevent bringing pathogens onto the farm.
- Rodent Control: Use traps or natural repellents to prevent rodents, which can carry diseases.
Solution: Develop a biosecurity plan and enforce it consistently. Consider quarantine periods for new or sick birds to prevent disease spread.
Example: A farm that implemented strict rodent control and quarantined new chickens reduced disease outbreaks by 40% over two years.
5. INADEQUATE RECORD KEEPING
Detailed record-keeping allows farmers to monitor productivity, manage costs, and identify trends. Many farmers overlook this aspect, making it difficult to make informed decisions.
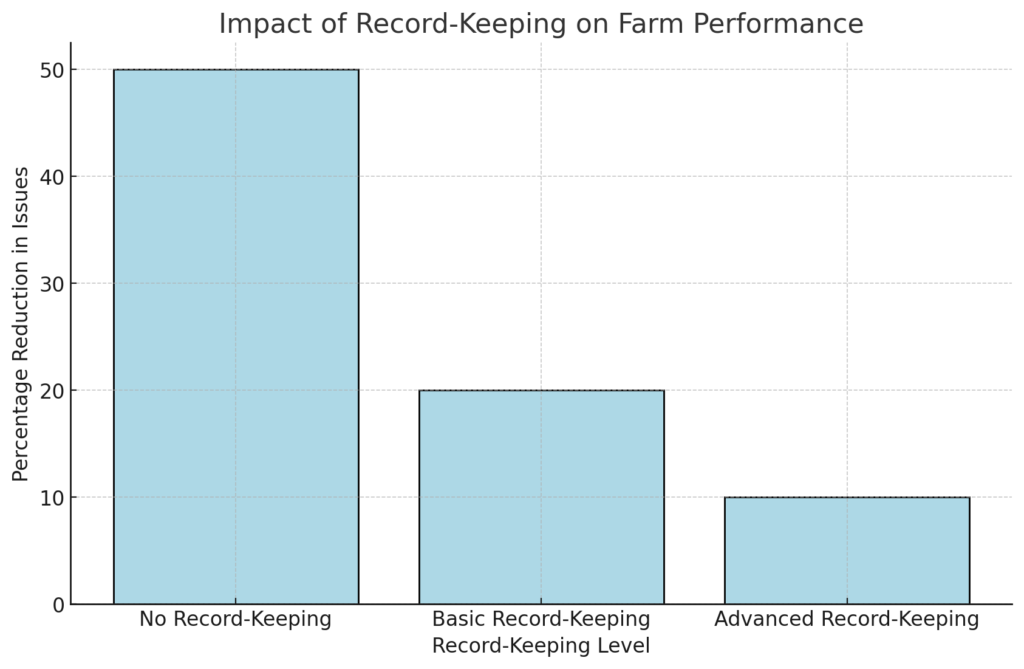
Column Chart: Farms with no record-keeping face a 50% increase in issues, while advanced record-keeping reduces issues by 10%.
Types of Records to Maintain
- Daily Feed Logs: Record the type, quantity, and cost of feed used each day.
- Egg Production Logs: Track daily egg production, noting sizes and any abnormalities.
- Health Records: Record vaccinations, treatments, and any health checks.
Solution: Use digital tools or apps designed for poultry management to automate record-keeping and data analysis.
Example: By maintaining a daily feed log, a farm in Missouri identified inefficiencies in feed distribution, saving 15% on feed costs in one year.
6. OVERLOOKING REGULATORY COMPLIANCE
Staying compliant with organic regulations is essential for certification and market access. Non-compliance can lead to penalties, loss of certification, and reduced consumer trust.
Solution: Regularly review guidelines from USDA Organic and conduct self-audits. Keep records of all organic practices, inputs, and certifications for verification.
Example: A farm in California, which prioritized compliance, increased sales by 30% after earning a recognized organic certification that expanded their market reach.
7. INCONSISTENT WATER SUPPLY
Water plays a critical role in chickens’ metabolic functions and egg production. Inconsistent supply not only causes dehydration but can also lead to stress, affecting the overall health and productivity of the flock.

Graph: Consistent water supply results in higher egg production, while irregular supply decreases yields.
Effective Water Management Tips
- Regular Cleaning: Clean water containers daily to prevent contamination.
- Additives: Use apple cider vinegar to improve water quality and boost immunity.
- Automatic Systems: Install automatic watering systems to ensure constant supply.
Solution: Ensure a constant supply of fresh, clean water. Monitor water levels frequently, especially during hot weather.
Example: A farmer in Arizona installed a rainwater harvesting system, saving 20% on water costs while maintaining consistent supply.
8. INADEQUATE MARKETING STRATEGIES
Marketing is essential for organic farms to grow their customer base. A lack of marketing efforts can lead to low sales and missed opportunities.
Advanced Marketing Strategies
- Social Media Ads: Use targeted ads to reach local customers interested in organic products.
- Content Marketing: Write blogs about organic chicken farming and share them on social media to engage with potential customers.
- Branding: Develop a unique brand identity that highlights the benefits of your organic products.
Solution: Combine online and offline marketing strategies for maximum reach. Engage with customers regularly through social media and email campaigns.
Example: A farm in Illinois launched a comprehensive digital marketing campaign, which led to a 60% increase in sales within a year.
9. NEGLECTING ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
Sustainability is a core principle of organic farming. However, some farmers focus too much on productivity and neglect environmental practices, which can harm long-term farm health.
Solution: Implement eco-friendly practices like composting and rotational grazing to maintain soil health and reduce environmental impact.
Example: A farm in Oregon that prioritized sustainable practices like water recycling and composting reduced operational costs by neglecting sustainability can have long-term repercussions on soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation, ultimately affecting overall productivity. For instance, a farm that prioritizes short-term productivity gains over sustainable practices can suffer from soil degradation, reduced crop yields, and increased pest problems.
Key Sustainable Practices to Implement
- Rotational Grazing: Moving chickens across different sections of pasture helps preserve grass quality, prevents overgrazing, and reduces soil erosion.
- Water Recycling Systems: Reuse rainwater for cleaning coops and providing supplementary water for chickens, reducing water bills and environmental impact.
- Organic Composting: Use chicken manure to create nutrient-rich compost, which can be used to fertilize pastures, improving soil health and reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
Solution: Prioritize sustainable methods, even if they require additional effort or investment. In the long run, sustainable practices lead to healthier chickens, better productivity, and lower costs.
Example: A farm in Oregon adopted rotational grazing, rainwater harvesting, and organic composting, reducing operational costs by 25% and increasing soil fertility over two years.
10. FAILURE TO INVEST IN TRAINING AND EDUCATION
Organic farming is continuously evolving, with new methods, technologies, and regulations emerging regularly. Failure to stay updated can result in outdated practices, inefficiencies, and missed growth opportunities. Training not only helps farmers understand the latest techniques but also boosts confidence and decision-making capabilities.
Benefits of Investing in Training
- Improved Disease Management: New training can introduce advanced biosecurity measures and disease prevention strategies, reducing mortality rates.
- Better Feed Management: Learn about new feed formulations or natural supplements that can boost productivity and health.
- Access to Grants and Subsidies: Some training programs offer information about grants and subsidies for organic farming, helping to lower costs and expand operations.
Solution: Regularly attend online courses, workshops, and farming expos. Joining organic farming communities can also provide a support network, offering resources and knowledge sharing.
Example: A farmer in Pennsylvania attended a two-day workshop on organic poultry nutrition, which led to a 20% increase in egg quality and production within a few months.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Organic chicken farming offers immense potential, but success depends on a commitment to learning, adaptability, and strategic management. Avoiding common mistakes like choosing the wrong breed, using low-quality feed, or neglecting biosecurity measures can improve productivity and profitability. Additionally, focusing on sustainability and investing in marketing and education ensures long-term success.
This comprehensive guide covers the essential aspects of organic chicken farming, providing solutions to common challenges. By implementing these strategies, farmers can enhance farm performance, maintain compliance, and attract a growing market of health-conscious consumers.




good
interesting
very good
Nice
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.