OVERVIEW
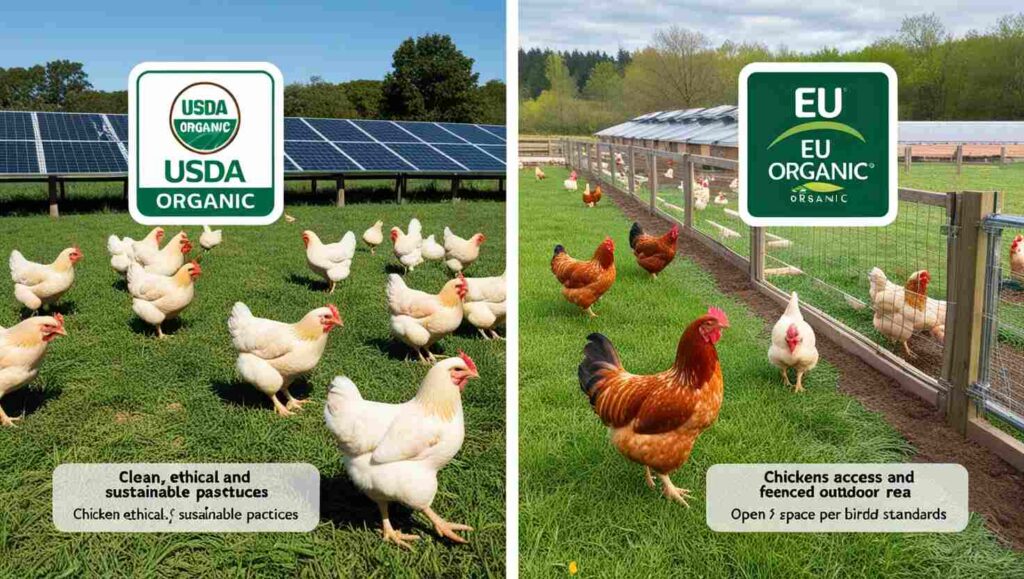
Organic chicken farming is governed by strict guidelines to ensure ethical, environmentally sustainable, and health-conscious practices. In the United States, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) oversees organic standards through the National Organic Program (NOP), ensuring compliance across areas like feed, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability. The USDA has the authority to conduct regular inspections and enforces these standards through accredited certification agents. If a farm fails to meet USDA organic standards, the USDA can revoke organic certification, which prevents producers from marketing products as organic, significantly impacting their market value and consumer trust.
In the European Union, the European Union Organic Certification operates under the European Commission. This regulatory body enforces EU-wide organic standards, focusing on animal welfare, feed requirements, and environmental practices. The EU’s standards are often more detailed regarding animal welfare, requiring outdoor access and specific space per bird. The European Commission can impose penalties, suspend certifications, and, in severe cases, disallow operations from using the organic label within the EU market if they fail to comply with regulations.
These two organizations not only enforce organic guidelines but also play a crucial role in promoting sustainable farming practices, thereby influencing global organic farming standards.
ORGANIC CERTIFICATION AND COMPLIANCE
United States
In the U.S., the USDA’s NOP establishes the standards for organic chicken farming. The program requires farmers to use organic seeds, manage livestock organically, and adhere to sustainable practices. Certification is provided through private certifying agents that are accredited by the USDA. These agents inspect farms to ensure compliance with the standards, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of organic farming.
If a farmer fails to comply with these regulations, the USDA can take several actions. This includes issuing fines, requiring corrective actions, or revoking organic certification altogether. The latter would prevent the farm from selling its products as organic, resulting in a significant financial setback.
For more information on USDA organic certification, you can visit the USDA National Organic Program.
European Union
In the EU, the European Commission oversees organic farming through regulations that apply to all member states. Organic certification in the EU is more centralized, and it requires compliance with strict guidelines that are often more comprehensive than those in the U.S. For example, the EU requires a minimum stocking density and mandates that organic poultry must have outdoor access.
Failure to meet these standards can result in serious consequences, including suspension of organic certification and potential legal action. The European Commission has the authority to enforce regulations and impose fines on non-compliant farms.
You can find more details on EU organic farming regulations at the European Commission Organic Farming page.
FEED REGULATIONS
USA
The USDA’s organic standards require that all feed given to organic chickens must be 100% organic, free from synthetic additives and GMOs. This includes restrictions on the use of certain feed ingredients that may not meet organic standards. Additionally, farmers are encouraged to provide a varied diet to ensure the health and well-being of the birds, which can sometimes lead to higher feed costs compared to conventional farming practices.
EU
In the EU, the requirements for organic feed are even more stringent. Not only must feed be 100% organic, but it must also be sourced from certified organic producers. The EU prohibits the use of synthetic amino acids and promotes the use of alternative protein sources, such as insects, to enhance sustainability. This strict adherence to organic feed standards is aimed at ensuring that organic poultry farming practices are environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Table 1: Comparison of Feed Regulations in the USA and EU
| Regulation Aspects | USA | EU |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Source | 100% organic, no GMOs | 100% organic, Local sourcing required |
| Synthetic Additives | Allowed under specific conditions | Prohibited |
| Alternative Proteins | Not specifically regulated | Encouraged (e.g. insects) |
ANIMAL WELFARE STANDARDS
USA
Animal welfare is a critical component of organic chicken farming in the U.S. The USDA requires that organic chickens have access to the outdoors, but the interpretation of “access” can vary. The regulations focus on the overall health and welfare of the birds, allowing farmers some flexibility in their practices. However, concerns have been raised about the actual living conditions of organic poultry, as some farms may not provide adequate outdoor space.
EU
In contrast, the EU’s animal welfare standards for organic poultry are much more detailed and rigorous. EU regulations require that organic chickens are provided with a minimum amount of space both indoors and outdoors. Each bird must have access to outdoor areas that promote natural behaviors, such as foraging and dust bathing. The emphasis on animal welfare in the EU reflects a broader societal commitment to ethical farming practices and consumer demands for humane treatment of animals.
Table 2: Summary of Animal Welfare Standards
| Welfare Aspects | USA | EU |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor Access | Required but variable | Required with specific space |
| Minimum Space per Bird | Not strickly defined | Defined (e.g. 4m² per bird) |
| Natural Behavior promotion | Encouraged | Mandated |
ENVIRONMENTAL AND SUSTAINABILITY STANDARDS
USA
In the U.S., while the USDA promotes sustainability, the guidelines are often less specific than those in the EU. Farmers are encouraged to adopt practices that reduce environmental impact, such as minimizing waste and using renewable resources, but there are fewer regulatory mandates. Some U.S. programs provide incentives for sustainable practices, but the integration of sustainability into organic farming is not as thoroughly regulated.
EU
The EU places a strong emphasis on sustainability in organic farming. The European Commission supports various initiatives aimed at reducing the environmental impact of agriculture. For example, the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) provides subsidies for farmers who adopt sustainable practices. Additionally, projects like the GreenChicken initiative are designed to explore sustainable feeding strategies, promoting the use of locally sourced organic feed and alternative protein sources.
KEY DIFFERENCES AND CHALLENGES
When comparing organic chicken farming in the USA and EU, several key differences stand out:
- Regulatory Rigor: The EU generally has more stringent and detailed regulations compared to the USDA, particularly concerning animal welfare and environmental sustainability.
- Flexibility vs. Strictness: U.S. guidelines offer more flexibility in certain areas, such as outdoor access for poultry, while the EU has strict requirements to ensure humane treatment.
- Market Demand: The consumer demand for organic products varies significantly between the two regions, affecting how farmers approach organic farming. In the EU, consumers tend to prioritize animal welfare and environmental sustainability more heavily than in the U.S.
These differences can create unique challenges for farmers operating in each region. For example, U.S. farmers may struggle with the perception of organic products if they do not meet consumer expectations for animal welfare, while EU farmers face higher operational costs due to stringent regulations.
Understanding the organic chicken farming guidelines in both the USA and EU is crucial for producers looking to operate within these frameworks. The USDA and the European Commission play pivotal roles in shaping the standards that govern organic farming practices, influencing everything from feed regulations to animal welfare and sustainability. As consumers become increasingly conscious of the origins of their food, adherence to these guidelines becomes even more significant for farmers aiming to maintain their organic certifications and meet market demands. By navigating the complexities of organic farming standards in these regions, producers can better position themselves in the growing organic market while contributing to sustainable agricultural practices.




Pingback: Healthy breakfast ideas- Keep Good your Heart for Daily Life
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.